As humans, we have some skills that seem so natural to us that we rarely think about them.
For example, sight. You probably thank heaven you have it, especially when you find out more about the difficulties of being blind. You remember something from the anatomy lessons. That’s about it.
But how many times have you felt grateful for… seeing colors? Have you ever wondered how many colors you can see? Do your friends see more colors than you? Or can you boast that nobody else sees the world in such beautiful colors like you do? (And I’m not referring to those days when you found your true love.)
Answers to such questions are more unexpected than you think. And they can even change the way you see the world.
On this page:
Actually, what are the colors?
Light is made up of a mixture of waves with different frequencies and amplitudes. Phew, sounds so damn technical! Let’s make an analogy…

When you watch the sea, you see the waves coming ashore one after the other. Simply put, that movement of the sea is a wave.

If you throw a rock in a pool, you’ll see some kind of waves, but very small ones. They rise up incomparably less than the sea waves. The height to which they rise (and fall!) compared to the average is called amplitude.
When you throw a rock in the pool, there is a number of small waves flowing for, let’s say, 1 meter in 5 seconds. That is frequency. Sea waves come less often, so they have lower frequencies. (And your frequency to those courses you hate, I bet was even lower.)
If you stay in the water, without seeing, you can tell the difference between waves with different frequencies and amplitudes. Your sense of touch will send the brain enough information. (Unless a hell of a wave carries you away.)
Let’s go back to light. I said it is a mix of waves. Like sea waves, only you don’t see them. Or do you?! You would not believe it, but you can see them, only not as you’d expect.
Light waves that interest us now have frequencies between 4 and 8 × 1014 Hertz. If you don’t work in a technical field, perhaps “1014 Hertz” doesn’t tell you anything. Let me translate: 100.000.000.000.000 of waves in a second!
Even light waves are shaped like the ones in water, but in 2 ways: electric and magnetic. Because light is composed of electromagnetic waves, while water waves are mechanical waves. I’m not gonna go on about all the differences between them. What’s important is that light is made up of waves at incomparably greater frequencies than mechanical waves.
Your brain does not have a processing speed high enough to realize what a real-time electromagnetic wave looks like. No matter how much you focus your attention, its frequency is so high that you have no chance of seeing anything. (In fact, the human brain can not even imagine what light looks like fundamentally, being both a wave and particle. The greatest minds still struggle to understand it.)
Light is very important for life, for many reasons, so it can not be ignored. And the brain is very clever. If it can’t see what these light waves look like, it thought of measuring their frequency. Taking into account that skin can not sense a fine “tickling” as that of light waves, another sensor appeared: the retina (with the eye assembly). And because all things must bear a name, these sensations caused by different frequencies of light were called colors.
You live surrounded by an ocean of light, whose waves also break on the beaches of your eye’s retina. And you only notice the sea foam.
I don’t know if you get it: each color is nothing more than what you successfully decipher from the form of various light waves!
How exactly can you distinguish colors?
By now you know about colors, which are the “tickling” sensation made of light vibrations on the retina. Only that the light that gets into the eye doesn’t only have a single frequency that you can measure (as you do with temperature). It is a flood of photons – and each one has a different frequency.
To explain this madness, the retina has several types of photoreceptor cells. The ones responsible for color perception are called cones.
Normally, the human eye has three types of cones – which were approximated as being specialized on certain colors red, green, and blue. Basically, you only see these three colors well – which means the stimulus produced by the corresponding cones is maximum for them 1)”Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems” by Lauralee Sherwood, edition published by Brooks Cole in 2015.

But the great trick to see more colors is that the three basic colors can be mixed within each other in different proportions. Kinda like when mixing watercolors.
This way of seeing, based on only three colors, is called tricromatism.
Digital photo/video cameras imitate the same trick. Only that instead of cones, the sensor in the camera has three cells for each pixel in the image. Its advantage is its organized distribution such as that of a math sheet. But in the eye, the cones are denser in center and more rare at the periphery. The distribution is “natural” – i.e. without accuracy.
Once the cones are stimulated by light waves, they transmit signals to the brain through the optic nerve. Basically, some electric “pinches” reach the brain. These are interpreted as representing one color or another.
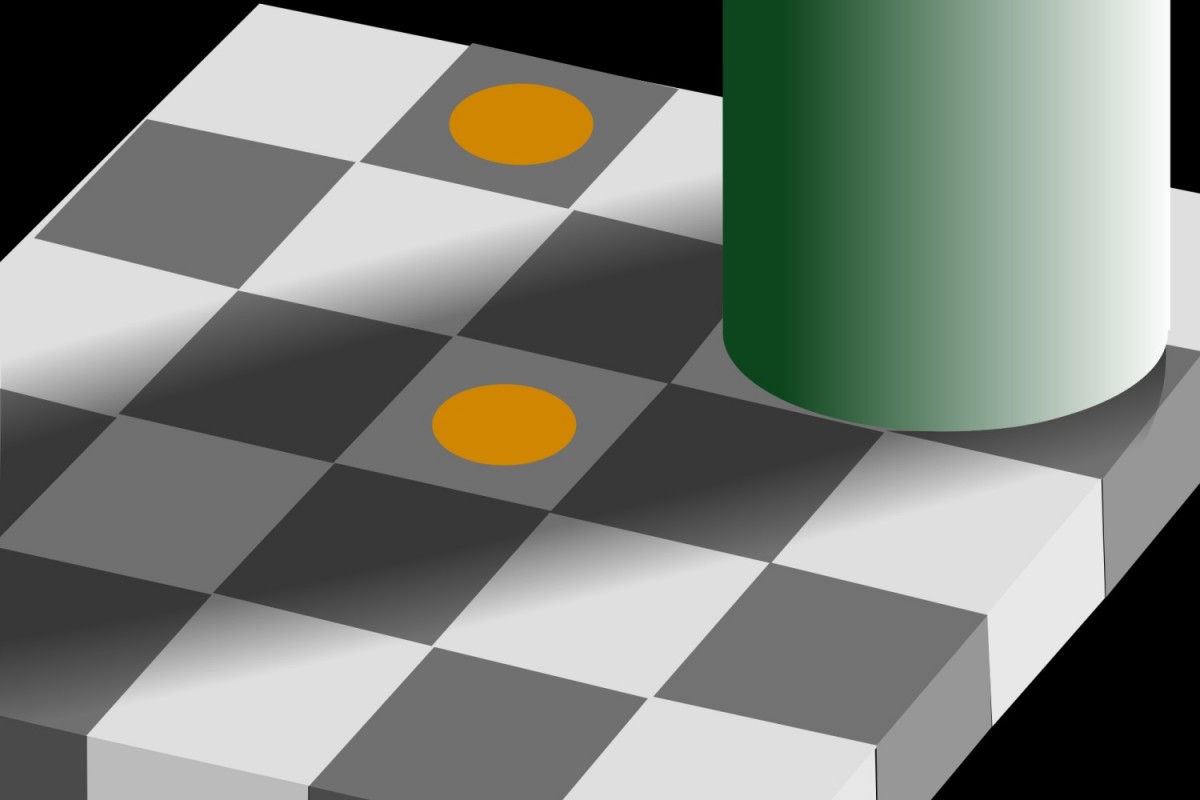
Let’s do a little test. Are the two dots in the image below the same color or are they different?
Even if you find it hard to believe, I tell you: they are identical. You see them in different shades because your mind does not fully listen to the eyes, but it makes all kinds of adjustments. If you are good at using professional cameras: you don’t see the raw picture, but one passed through Photoshop.
Let me reiterate for you so you don’t lose sight of the amazing story: from the outside you just perceive signals about 3 colors in different intensities. All colors are formed in your mind!
How many colors can you see?
Specialists estimate that a cone can differentiate about 100 levels of intensity 2)”Some women may see 100 million colors, thanks to their genes” by Mark Roth, article published in Pittsburgh Post-Gazette on September 13, 2006. That means shades of that color. (It might have a greater number, but no one knows exactly how many, so let’s not complicate this situation more than it needs to be.)
A normal man has three kinds of cones, the total number of colors he can see (including shades) is:
100 × 100 × 100 = 1.000.000
Before exploding with delight or lifting your eyebrows with confusion, I must say that this is the potential. I mean you can see a million colors exactly the same way you can lift 650 kilograms 3)”Watch ‘Game Of Thrones’ Hafthor Bjornsson Break 1,000-Year-Old Viking Record, Lift 1,400-Pound ‘Monster Log’” by Thomas Barrabi, article published in IBT Pulse on February 4, 2015. I mean, you could, but…
Let’s start from the beginning. When you were born, you had everything you needed to see colors. And yet, you didn’t see them. Newborns see only in black and white.
The brain must learn how colors work. How to interpret electrical impulses through the optic nerve to know which one represents a certain color. And then to paint some beautiful pictures. The job of an artist.
Every child teaches himself to sing. How he sings – that’s another story. The same thing happens with seeing color: till some point, you can handle yourself, but after that it’s a matter of education. The difference between this and singing is that no one sees what you see. You have no idea if the person sitting next to you sees the same things in more (or less) shades than you do. Or maybe his colors are more vivid (or darker). Or perhaps the color accent is more red, or green, or blue. Or maybe his mind receives very similar signals, but interprets them differently.
The number of shades that you actually get to see depends on various factors:
- physical quality of vision
- intellectual development
- how often you pay attention to shades
- awareness of the shades and how they harmonize
- the number of shade names you know and how often you use them
- being instructed in a branch of visual arts that require color
- variety of colors that you have to deal with daily
In short: exercise. The same thing you do with your muscles. In fact, with everything.
One thing is certain: the colors you see are only yours. No one sees in exactly the same shades.
Some people see less colors
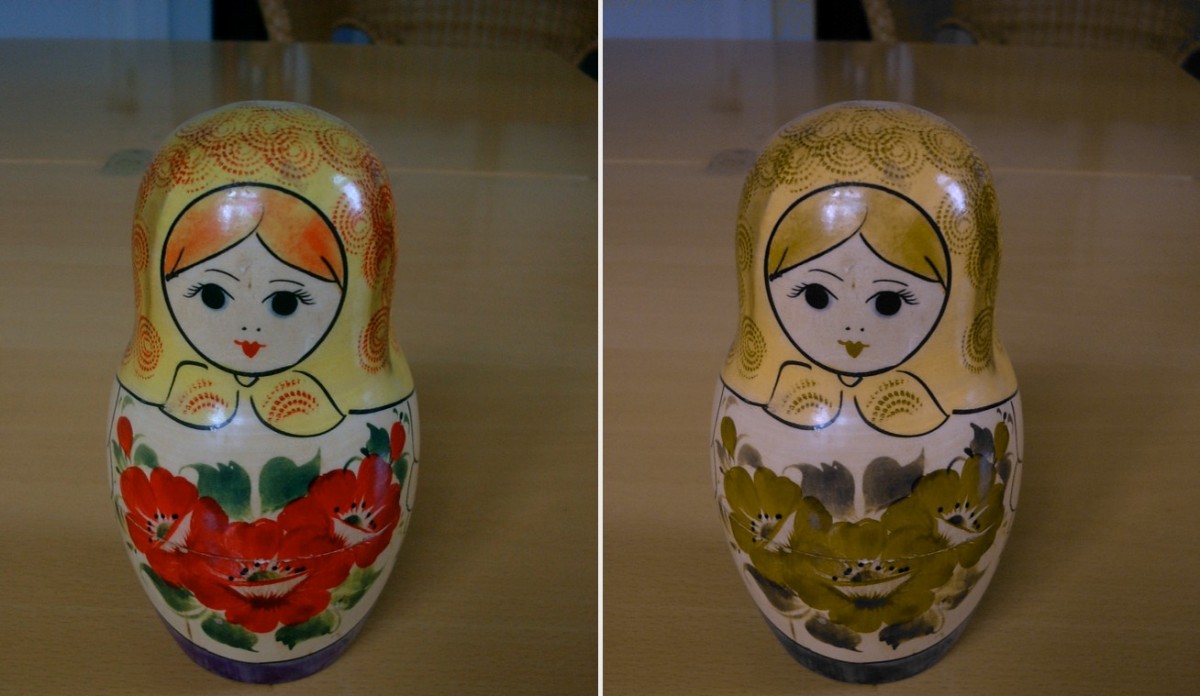
You’ve probably heard of color blindness. Scientifically it’s called color vision deficiency. It is a sight disorder that makes the shades of red look something like those of green.
The reason is simple: either the cones for red, or the cones for green have suffered a mutation, or they are absent 4)”The genetics of normal and defective color vision” – study conducted by Jay Neitz and Maureen Neitz, published in Vision Research on April 13, 2011.
Interesting is the fact that about 7% of men are affected, but only 0.4% of women. Because women have the joy of shopping, so they can’t get tangled in colors.
Those who have only two types of cones or those whose third cone is like non-existent, is called dicromatism. What do you think happens to the number of colors? Let’s look at the previous calculation:
100 × 100 × 100 = 10.000
Big difference!

Let’s take a common example (in movies): you’re in an airplane and you just found a time bomb that will explode soon. The specialist from the ground says, “Don’t worry! You have a red wire and a green wire. You just have to cut the red wire. Do not, by any circumstance, cut the green one!” But you are color blind. Luckily modern technology rescues you. There are smartphone apps that process a picture so that those who are color blind can distinguish when the eye doesn’t. You take a picture and you know what wire has to be cut.
In cases where the cones are not completely missing, but behave abnormally to some extent, the brain can be helped with special glasses that change the shades that can not be visibly seen without them. Although there is no perfect solution for every situation, for those who could never distinguish red from green, it’s like gaining special powers 5)”A Scientist Accidentally Developed Sunglasses That Could Correct Color Blindness” by Li Zhou, article published in Smithsonian Magazine on March 3, 20156)”Glasses That Solve Colorblindness, for a Big Price Tag” by David Pogue, article published in The New York Times on August 15, 2013.
There are also cases, pretty rare indeed, when some people do not perceive colors at all. Everything they see is black and white, like an old television. Their view is called monocromatism.
When you don’t have such problems, colors seem so natural to you, that you don’t think about how lucky you are for seeing them. Try to remember that when you look at a flower garden. Or at a rainbow.
Some women see an incredible amount of colors
Did it ever seem to you that women have a greater proclivity for color? From what was said above, you can draw the conclusion that, on average, it is correct. But some women just don’t have limits.

You know, superheroes have all sorts of incredible superpowers. It excites you, they seem like fantasies.
For example, what would someone with the superpower of seeing 100 times more shades be like? With the ability to see each surface more colorfully detailed? With a new understanding of space through color?
Well, that’s not a fantasy. Such people do exist. In fact, they are only women. I told you that women and colors have a special relationship.
After a study by Jay Neitz, a renowned researcher in this field, 2-3% of women have four kinds of cones, not 3 7)”Some women may see 100 million colors, thanks to their genes” by Mark Roth, article published in Pittsburgh Post-Gazette on September 13, 2006. This is what physicians call tetracromatism.
The implications can be major. As you know, it is sufficient to complete the formula for calculating the number of colors that can be distinguished:
100 × 100 × 100 × 100 = 100.000.000
Amazing, isn’t it?
And it’s not just the chromatic richness. These details give the brain more information to better estimate distances, forms, movements, etc. It is almost impossible for an ordinary man to understand, it’s like seeing in 4 dimensions. In fact, there are 4 dimensions, but chromatic.
In cases found so far, this fourth type of spectral cone is inserted between red and green. Usually corresponds to a kind of orange.
But there’s nothing precise. In some cases, additional cones collected frequencies very close to red, or green. So the person does not even realize that they have a fundamentally different view from others 8)”Some women may see 100 million colors, thanks to their genes” by Mark Roth, article published in Pittsburgh Post-Gazette on September 13, 2006.

Concetta Antico was a little Australian girl with talent in painting; this is when she realized that her view was different than others. But it differed in a way that was useful to her talent. So she made her artistic abilities into her career. Two decades passed before she learned in 2012 that her eyes have 4 types of cones. And since then she has become the most well-known person to have this ability 9)”This Woman Sees 100 Times More Colors Than The Average Person” by Alexandra Ossola, article published in Popular Science on October 13, 201410)”Condition Called Tetrachromacy Allows This Artist To See 100 Million Colors” by Lisa Winter, article published in IFLScience on October 15, 2014. In her paintings, she tries to represent what she sees – and the result is very interesting. Some can be seen on her official website.
It seems great to see so many colors. And it can even be useful. On the other hand, it is very tiring. The brain has to process significantly more information. And the brain can barely pay attention to the common view around it, so something more can be overwhelming. Experts assume that if someone can see these additional colors, they are likely to be mentally ignored. Concetta Antico was lucky that her rare ability was easily combined with her talent and artistic training 11)”The women with superhuman vision” by David Robson, article published by BBC on September 5, 2014.
Colors that you don’t see

Beings who have four types of cones on the retina are called tetracromats. It is not specific to humans; on the contrary. We know that birds such as doves, pigeons, and zebra finch, as well as fish such as goldfish and zebrafish are tetracromats. And these animals even do better, because they have the fourth type of cones for ultraviolet light. In other words, they see colors that you will never see.
It’s like in the case of sound. You can hear a high note. Or one even higher. But if the notes keep growing, at some point you no longer hear them. It goes as far as the auditory spectrum.
Also sight has such limits, chromatic ones.
You know that the TV remote works with infrared. What are those? The remote is a flashlight. When you click a button, it emits some flashes. Just like back in the day when those who communicated from one hill to another flashed lights to each other. But in order to not bother you, the light emitted by the remote control is infrared, which means it has a lower frequency than red. Red is the lower limit of the visual spectrum (like bass for sounds), so what ever is below red cannot be seen. So, whenever you press a button on the remote, the room is filled with a color you do not see. Do you begin to realize that something happens and you don’t know about it?
The same thing happens at the other end of the visual spectrum. Beyond violet lies ultraviolet – another color that you cannot see.
But how much can we actually see from the entire light spectrum?
When you say “light”, usually you refer to visible light. But there is light you cannot see. In fact, physicists have found that all electromagnetic radiation can be called “light” because their only important differences is related to frequency. Even radio waves, which are at the lower end of the electromagnetic spectrum, can be considered a form of light. Their frequency is much smaller than the one of visible light, but they behave the same: they reflect, refract, etc. Why do you think you can hear or see a live show on radio or TV? Because radio waves travel with the speed of light.
I’m not trying to convince you that you’re losing something because you don’t see the “colors” from the radio waves or microwaves spectrum. Or, at the opposite end of the spectrum, X-ray and gamma ray “colors”. Perhaps you cannot imagine them being associated with colors. I’m not gonna insist on this.
But it’s easy to understand that there is light and colors that we, humans, can not see. However, some animals can. We humans are not the center of the universe to say that the colors we see are the only ones that exist. Especially since, as it has been proven, not even people see the same colors.
If we limit the definition of light to the one visible for us, plus ultraviolet and infrared, we get a spectrum between 3 × 1012 and 3 × 1017 Hertz. This range is so wide that the visible part is a hundred times smaller. Plainly said, you see colors through a keyhole – a small strip of what exists out there.
I’m gonna highlight: you only see a little part of the light moving around you. Objects transmit so much chromatic information that you cannot imagine. It’s like all your life you’ve seen black and white and then someone tells you about colors.
After all I’ve said to you, you’ve probably concluded that all colors are fiction. And from a certain point of view, they are.
You perceive reality through your senses. All you know about reality is a matter of interpretation. It is a translation of a translation.
But that’s all you’ve got. So it’s not so important how real colors are. You see them, give them names, you can use them. Moreover, you can enjoy them! They’re beautiful and you’re part of this miracle, because without you, they would remain some electromagnetic waves. Without a good story.
All about the development of vision in children, with fascinating facts about eyes.
References
| ↑1 | ”Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems” by Lauralee Sherwood, edition published by Brooks Cole in 2015 |
|---|---|
| ↑2, ↑7, ↑8 | ”Some women may see 100 million colors, thanks to their genes” by Mark Roth, article published in Pittsburgh Post-Gazette on September 13, 2006 |
| ↑3 | ”Watch ‘Game Of Thrones’ Hafthor Bjornsson Break 1,000-Year-Old Viking Record, Lift 1,400-Pound ‘Monster Log’” by Thomas Barrabi, article published in IBT Pulse on February 4, 2015 |
| ↑4 | ”The genetics of normal and defective color vision” – study conducted by Jay Neitz and Maureen Neitz, published in Vision Research on April 13, 2011 |
| ↑5 | ”A Scientist Accidentally Developed Sunglasses That Could Correct Color Blindness” by Li Zhou, article published in Smithsonian Magazine on March 3, 2015 |
| ↑6 | ”Glasses That Solve Colorblindness, for a Big Price Tag” by David Pogue, article published in The New York Times on August 15, 2013 |
| ↑9 | ”This Woman Sees 100 Times More Colors Than The Average Person” by Alexandra Ossola, article published in Popular Science on October 13, 2014 |
| ↑10 | ”Condition Called Tetrachromacy Allows This Artist To See 100 Million Colors” by Lisa Winter, article published in IFLScience on October 15, 2014 |
| ↑11 | ”The women with superhuman vision” by David Robson, article published by BBC on September 5, 2014 |
Did you like it? Now it’s your turn. You’ll make us very happy if you share this article with your friends:
And don’t forget to let us know what you think – we are really interested in your thoughts on this!